Framework
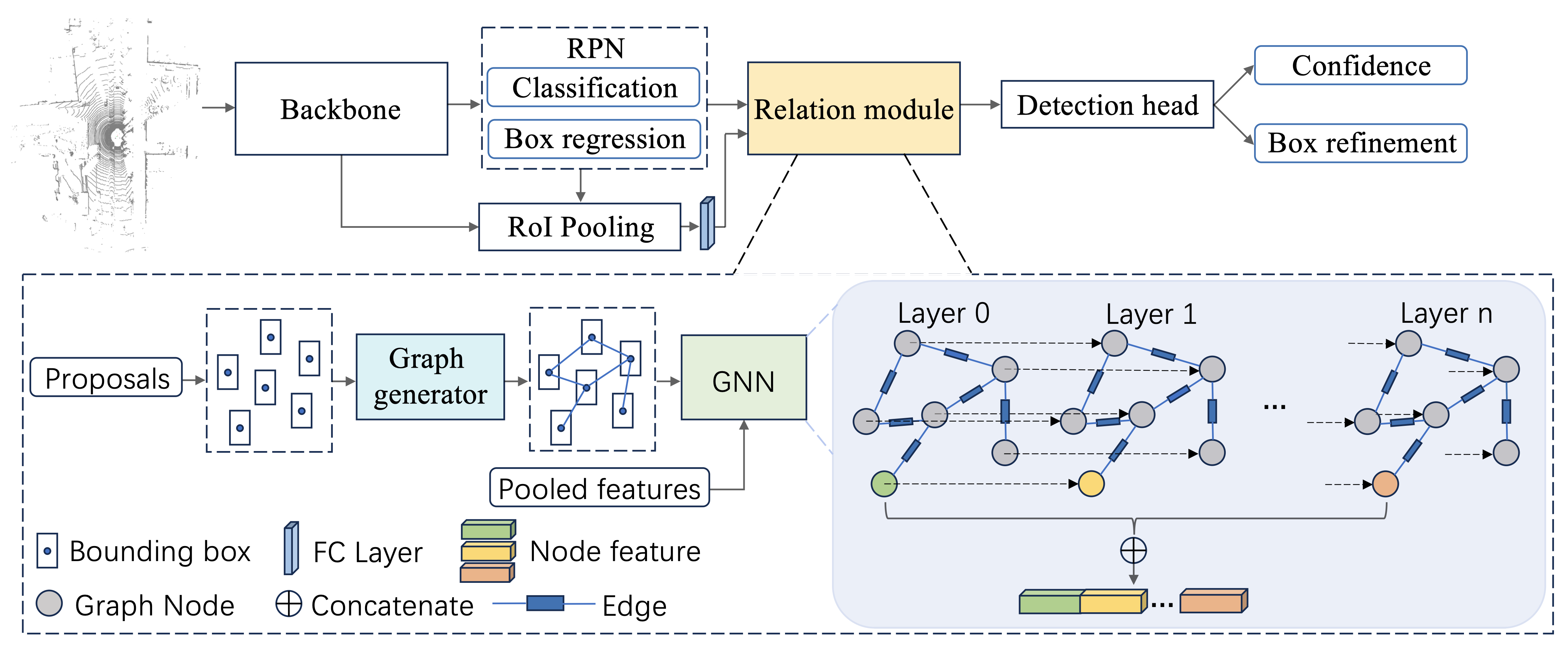

Accurate and effective 3D object detection is critical for ensuring the driving safety of autonomous vehicles. Recently, state-of-the-art two-stage 3D object detectors have exhibited promising performance. However, these methods refine proposals individually, ignoring the rich contextual information in the object relationships between the neighbor proposals. In this study, we introduce an object relation module, consisting of a graph generator and a graph neural network (GNN), to learn the spatial information from certain patterns to improve 3D object detection. Specifically, we create an inter-object relationship graph based on proposals in a frame via the graph generator to connect each proposal with its neighbor proposals. Afterward, the GNN module extracts edge features from the generated graph and iteratively refines proposal features with the captured edge features. Ultimately, we leverage the refined features as input to the detection head to obtain detection results. Our approach improves upon the baseline PV-RCNN on the KITTI validation set for the car class across easy, moderate, and hard difficulty levels by 0.82%, 0.74%, and 0.58%, respectively. Additionally, our method outperforms the baseline by more than 1% under the moderate and hard levels BEV AP on the test server.